
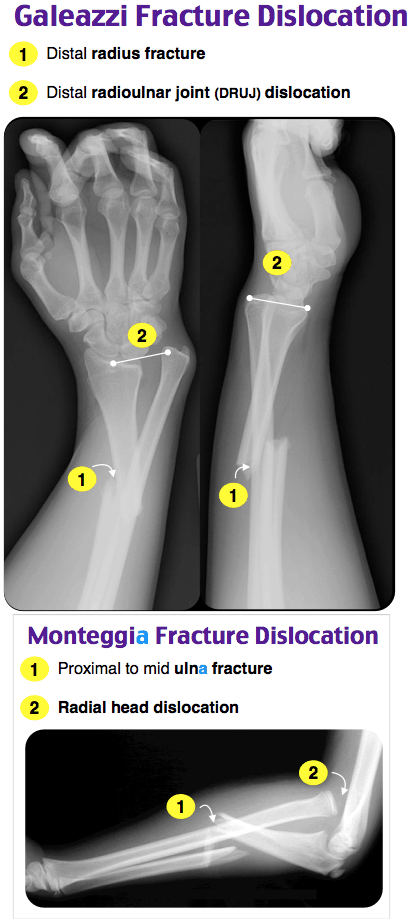
This is often due to the lack of experience of medical personnel and radiology technicians. Several cases of misdiagnosed Monteggia and Galeazzi fractures have been reported in the literature. In our medical observation, this principle was not respected which explains the misdiagnosis of the associated Monteggia and Galeazzi on the same limb. The diagnosis of Monteggia and Galeazzi ipsilateral fractures is mostly paraclinical by performing standard radiographs of the forearm showing upper and lower joints. In trauma resulting by road accident as in our patient, the mechanism is more complex.ĭelay was the cause of the issues observed in the functional result, in particular on the pronosupination function and the grip strength which are the main functions among the most important of the thoracic limb.įractures―bipolar dislocations of the forearm or “floating radial diaphysis” may result from a combination of direct and indirect mechanisms. Galeazzi fracture results from a direct dorso-radial impact on a forearm in forced pronation and an extended wrist. Ĭonsidering the traumatic mechanism, Monteggia fracture results from a direct impact on the ulnar diaphysis, producing dislocation of the radial head, and indirect shock by falling on the hand, with the wrist in extension. Isolated Monteggia and Galeazzi fractures is estimated at approximately 1% - 2% Monteggia and 3% - 6% of Galeazzi fractures. X-ray of the right forearm on the 12 th day following surgery. Their frequency has not been reported in the literature. Ipsilateral Monteggia and Galeazzi fractures constitute a very rare condition. The anatomy of the forearm bones was restored, but the flexion-extension of the elbow was quantified at 95˚ and −20˚ flexion-wrist extension quantified at 10˚ and 10˚, pronation at 15˚ and supination 20˚. 9 months after surgery, all fractures consolidated. The patient then underwent physiotherapy. This fracture was treated by screw plate of the ulna and trans-condyloradial pinning at the 11 th day of the trauma ( Figure 3).īoth pins were removed 30 days after the second surgery. Postoperative X-ray revealed a Monteggia fracture that was previously missed ( Figure 2). There was painful swelling in the right elbow.
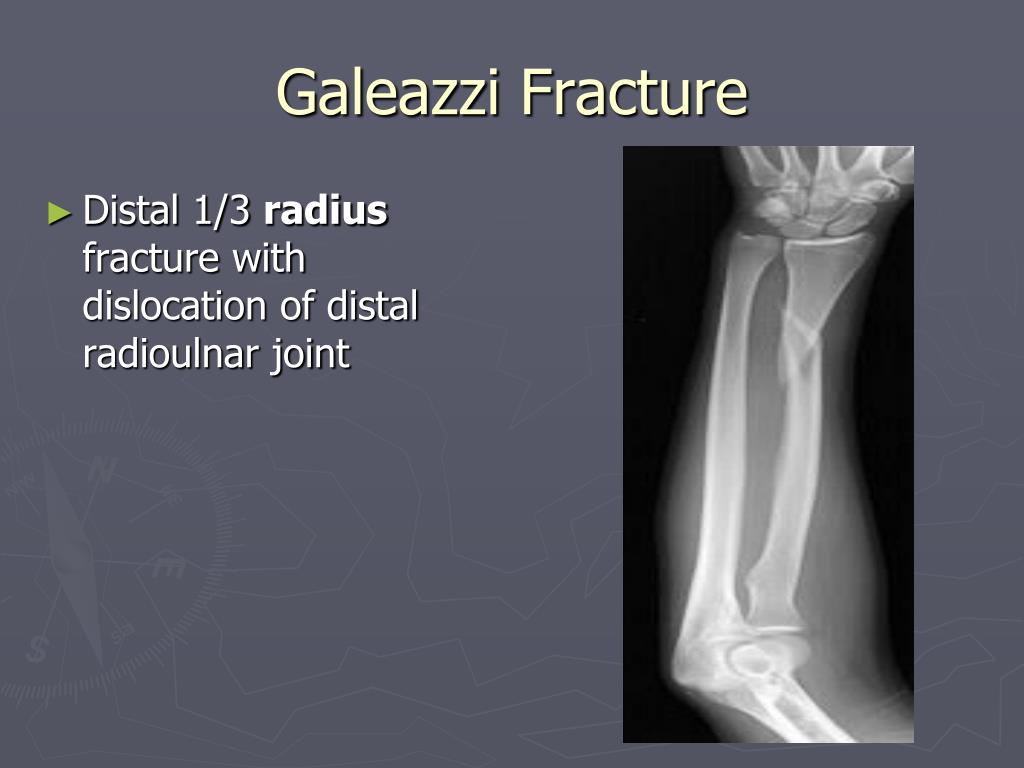
Twenty-four hours after the surgery, the patient experienced recurrent and severe pain. Due to financial issues the fracture was treated on the 5 th day of the injury by a screwed plate on the radius and the distal radioulnar joint was pinned by a Kirschner pin. X-ray of the right forearm did not show the elbow joint, but showed a Galeazzi fracture ( Figure 1). The sensitivity and motility of the limb were preserved.

Physical examination revealed swelling of the forearm, distortion of the right wrist and total impotence of the right limb. Upon admission, the patient complained of pain in the right forearm. We reported a case of an ipsilateral fracture of Monteggia and Galeazzi in a 45-year-old patient whose therapeutic delay caused a major post-surgical functional issue.Ī 45-year-old patient, with no pathological priors, was admitted at Brazzaville Teaching Hospital for severe trauma of the right forearm after a road accident. In adults, their management is surgical and is proposed early in order to restore the anatomy of the antebrachial skeleton, restore joints functions, restore pronosupination, and restore the flexion-extension of the elbow and wrist. Fractures of Monteggia or Galeazzi are often misdiagnosed when the radiographs of the forearm do not show the upper and lower joints. It is very rare and a few cases are reported in the literature. The association of Monteggia and Galeazzi fractures or bipolar fracture-dislocation of the forearm or “floating radial diaphysis” according to Jupiter was first described by Odena.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
